A Practical Guide to Minimally Invasive Vascular Treatments
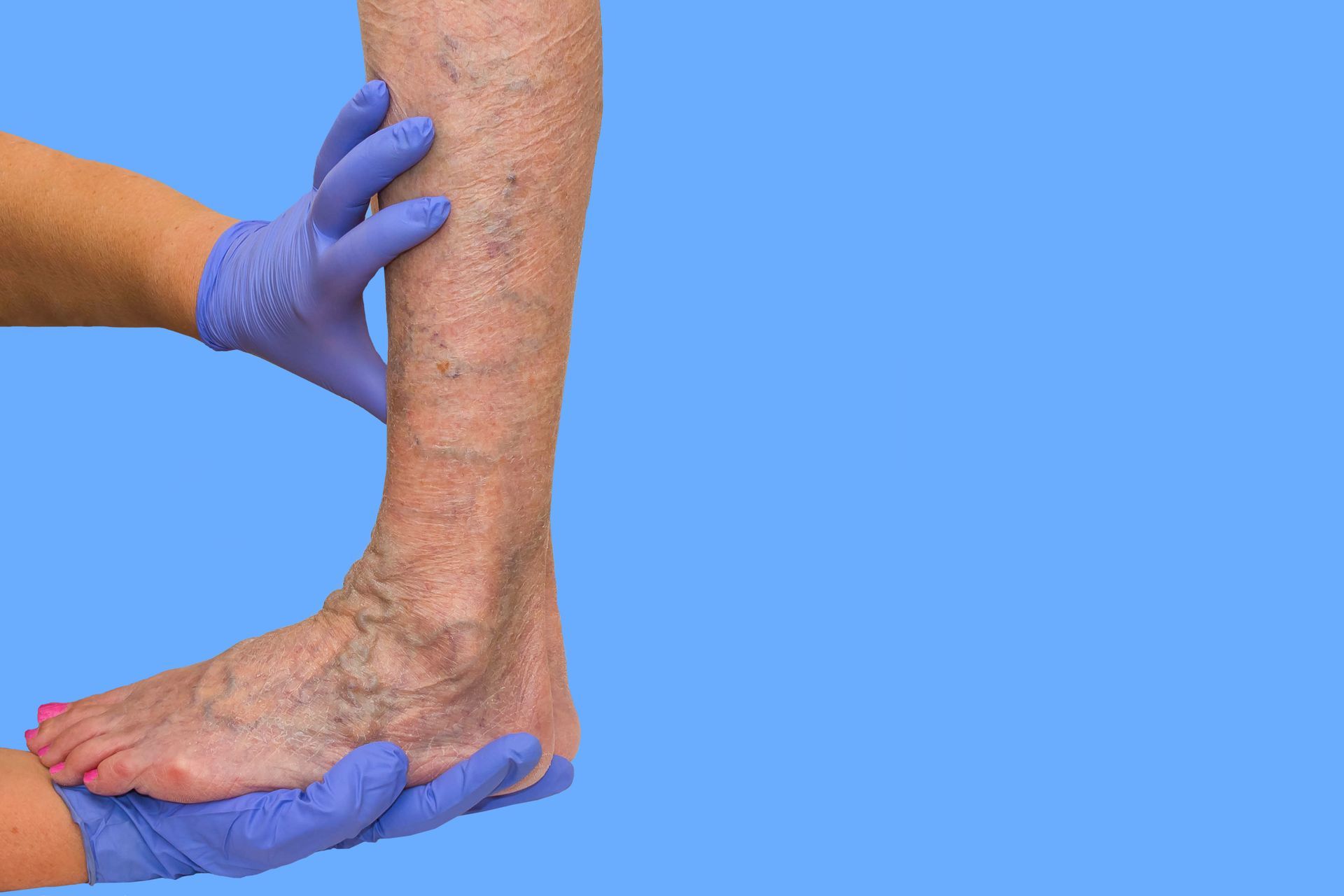
Chronic venous insufficiency, varicose veins, leg swelling, and circulatory problems can significantly impact mobility, comfort, and long-term vascular health. The good news? Modern vascular care no longer relies solely on invasive surgery. Today’s minimally invasive treatments offer faster recovery, reduced risks, and highly effective outcomes — often performed in-office with little to no downtime.
At California Vascular Health, our specialists focus on advanced, evidence-based procedures designed to restore proper blood flow and relieve vein-related symptoms with precision and comfort. This guide breaks down the most common minimally invasive vascular treatments and what patients can expect during care.
Why Minimally Invasive Treatments Are the New Standard
Traditional vascular surgery often required lengthy recovery and deep anesthesia. Minimally invasive therapy, however, uses targeted techniques such as lasers, ultrasound, and medical adhesives to close or repair diseased veins from within.
Benefits include:
- Little to no downtime
- Local anesthesia only
- Reduced pain and scarring
- Lower complication rates
- In-office procedures instead of hospital surgery
- Faster return to daily activities
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT)
EVLT is a leading treatment for varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency. Using ultrasound guidance, a thin catheter delivers laser heat to seal the damaged vein, redirecting blood flow to healthy vessels.
Ideal For: Bulging veins, leg fatigue, swelling, skin discoloration
Why Patients Choose It:
- Quick and precise
- Relief from symptoms like aching or heaviness
- Long-term success rates above 90%
- Minimally invasive alternative to vein stripping
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
Similar to EVLT, radiofrequency ablation uses controlled thermal energy — but from radiofrequency waves — to collapse diseased veins.
Best For: Moderate to severe venous insufficiency
Benefits:
- Minimal discomfort
- Rapid healing
- Proven safety and effectiveness
This method is often preferred when laser heat may not be ideal due to vein location or patient sensitivity.
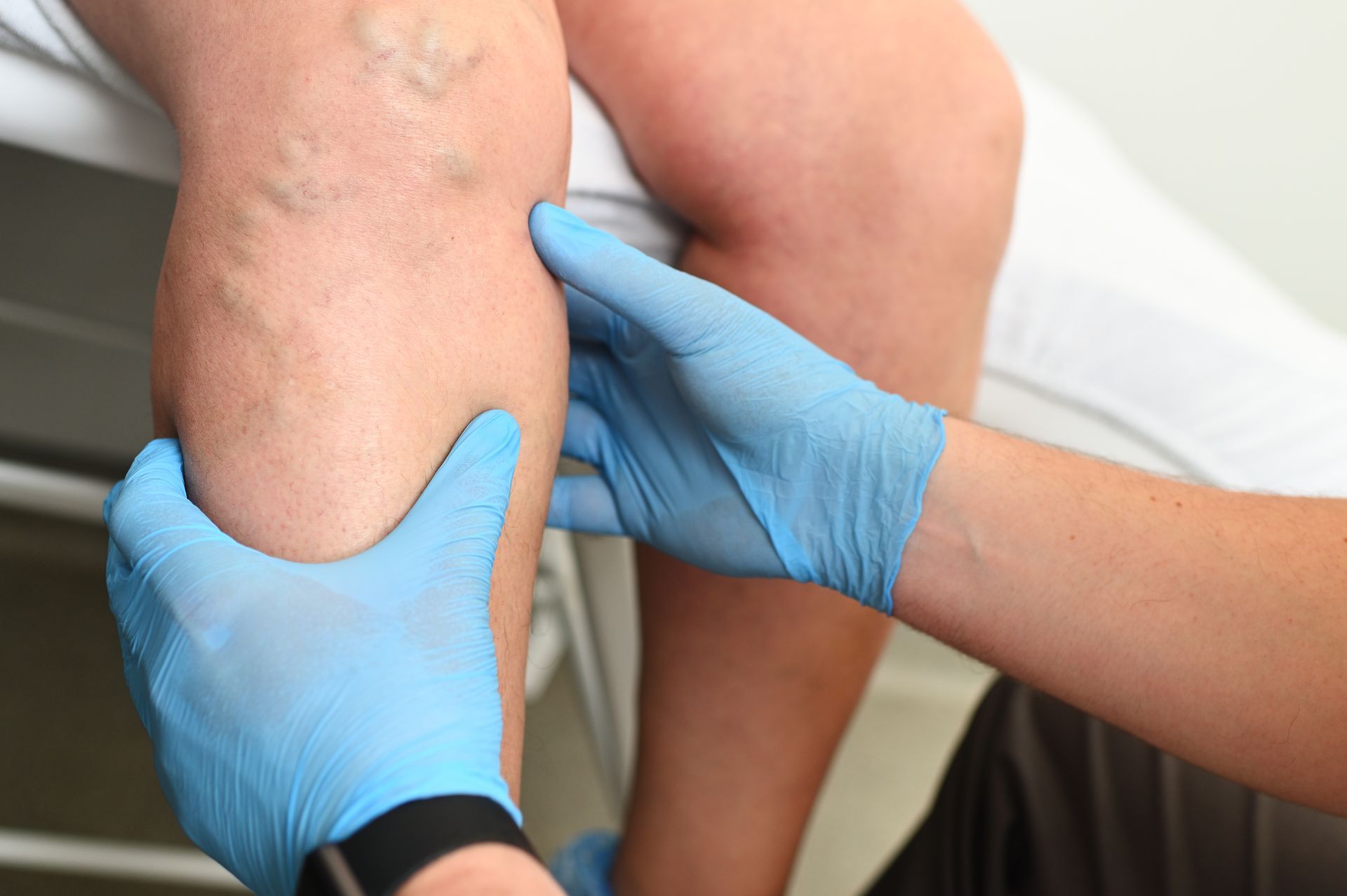
Sclerotherapy
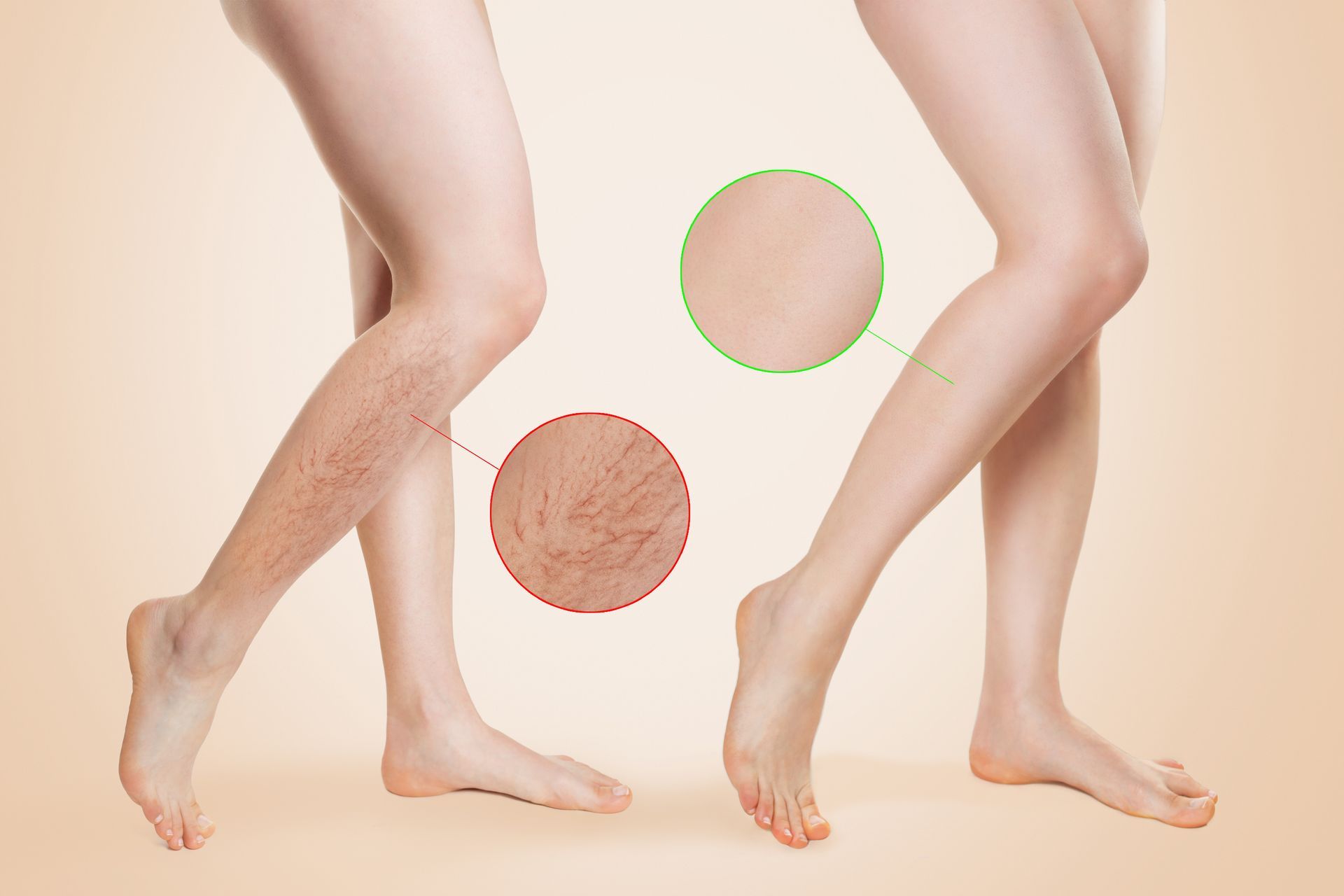
Sclerotherapy is one of the most commonly performed treatments for spider veins and small varicose veins. A medical solution is injected into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time.
Ideal For:
- Cosmetic spider vein removal
- Small-to-medium surface veins
- Post-EVLT supportive treatment
Benefits:
- No anesthesia needed
- Quick procedure (typically 15–30 minutes)
- Noticeable cosmetic enhancement
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
For veins that are larger or closer to the surface, phlebectomy removes varicose veins through tiny micro-incisions. It’s still minimally invasive and typically performed alongside EVLT or RFA.
Ideal For: Large, bulging varicose veins
Benefits:
- Precise vein removal
- Minimal scarring
- Immediate improvement in appearance
When to Seek Evaluation
You may benefit from minimally invasive vascular treatment if you experience:
- Leg pain or heaviness
- Swollen or throbbing veins
- Burning, itching, or cramping
- Skin darkening around the ankles
- Visible varicose or spider veins
- Slow wound healing or ulcers
Ignoring symptoms may worsen venous disease over time, increasing risk of clots or chronic leg swelling.
Why Choose California Vascular Health
Our practice combines board-certified vascular expertise with patient-focused treatment planning. Every care plan begins with diagnostic imaging to identify the underlying cause — ensuring results that are not just cosmetic, but medically effective.
What sets us apart:
- State-of-the-art in-office procedures
- Personalized treatment plans
- Comprehensive vascular diagnostics
- Focus on comfort, transparency, and long-term health
Take the First Step Toward Healthier Veins
Minimally invasive procedures make it easier than ever to improve circulation, reduce pain, and restore confidence in your legs. Whether you're seeking relief from chronic symptoms or treating visible veins, our specialists are here to help.